45
46
In calculating the air gaps at A and B in
Figure 5, the interference bands were counted
No Response Required
from the edge of the gage block which was in
contact with the surface of the optical flat.
The line formed by the gage block edge is ident-
ified in foldout-10 as the _____ _____ ________.
52
straight
53
We have implied that a gage block mating
flat
surface which is flat will produce interference
evenly
bands which are _______ , and a gage block mat-
spaced
ing surface which has a _________ ________ will
constant
cause the interference bands to be ____________
_____________ .
60
evenly
61
The interference bands near the outer edge
spaced
of the optical flat at B in foldout-12 increase
slope
in number and are spaced _________ together be-
constant
cause the ________ of the surface is steeper in
that area.
67
increase
68
You can see that the ______ of ______ at C
number
has
been shifted to the right of center. When
point
the
measurement at C is compared with A, you can
contact
see
that the bands at C have _______ in ________
spacing (distance)
and
are spaced __________ together.
interference
bands
75
height
76
Look at foldout-14. The illustration shows
how you place an ______ _______ over two blocks
to compare the height of a block being measured
with the ______ of a standard block so that you
can determine the difference in the heights of
the blocks.
83
84
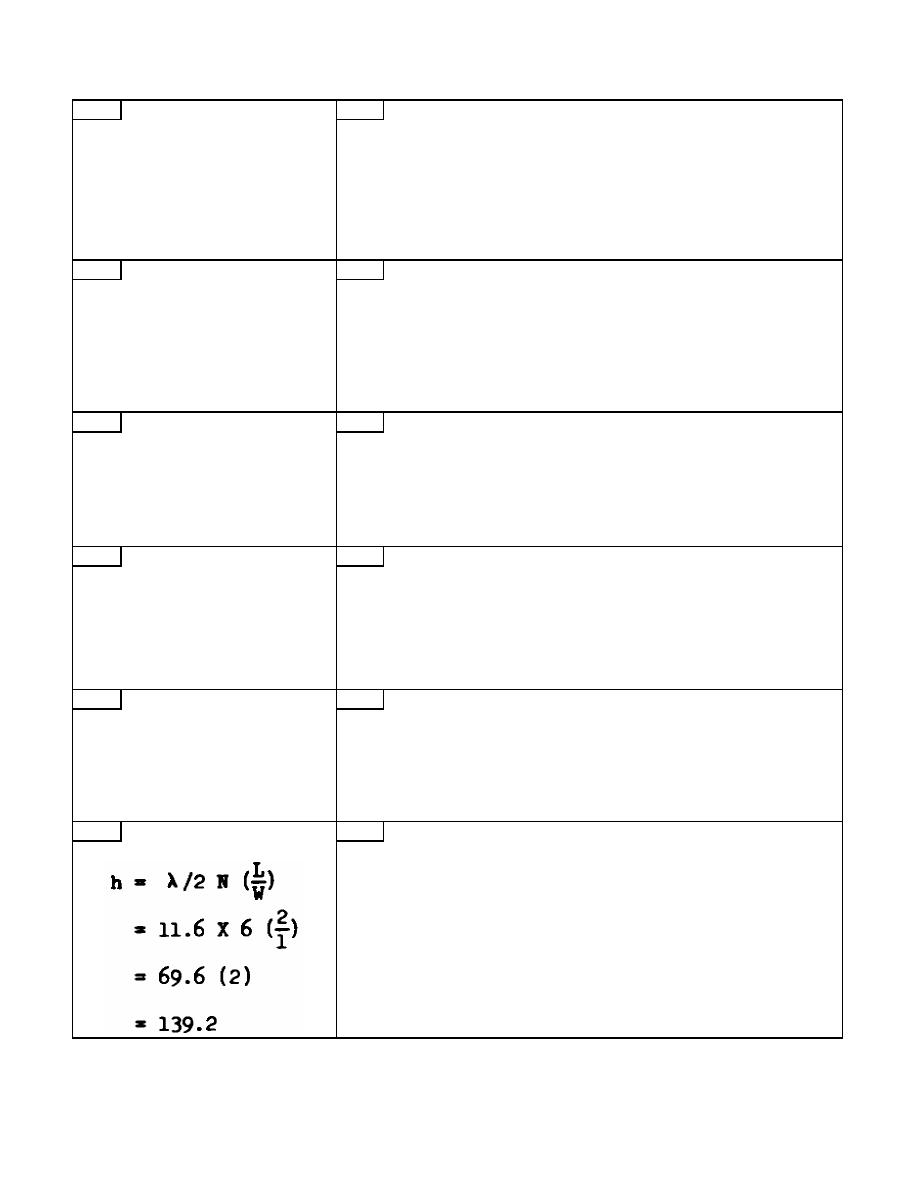
The height of block B can be determined by
adding the difference in heights of the two
blocks to height of the standard. If the height
of the standard is 0.050 inch, the height of
block B is ____________________ inch.
52



 Previous Page
Previous Page
