SM0486
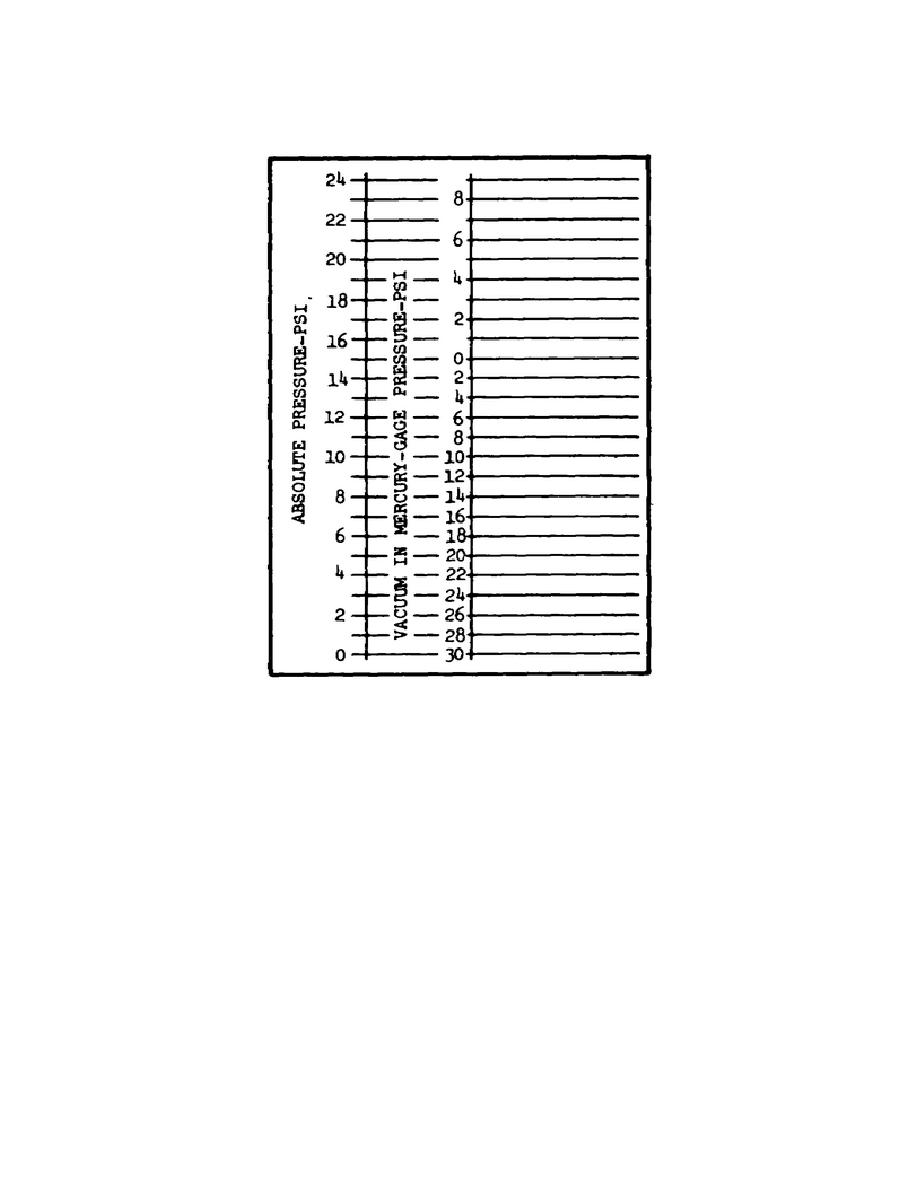
Figure 19.
Approximate Relationships of Reference Pressures
(3) In addition to establishing a relationship between absolute and
atmospheric pressures, Figure 19 also establishes the fact that vacuum
is based on atmospheric pressure; high vacuum approaches absolute zero,
low vacuum approaches atmospheric pressure. The conventional manometer
charts list pressures referenced to atmosphere.
Such readings are
known as gage pressures. As may be seen from an inspection of Figure
19, absolute pressures may be obtained from gage pressures by
determining the barometric or atmospheric pressure existing at a given
time and place and adding the gage pressure to the atmospheric
pressure. For example, look at the chart in Figure 19 and locate the
absolute pressure of 18 psia.
This value represents the sum of the
gage pressure (3 psi) and the approximate atmospheric pressure at sea
level (15 psia).
(4) We have studied the preliminary theories, conditions, and concepts of
manometer pressure measurement; now let's examine the principle on
which the operation of the well type manometer is based.
69



 Previous Page
Previous Page
