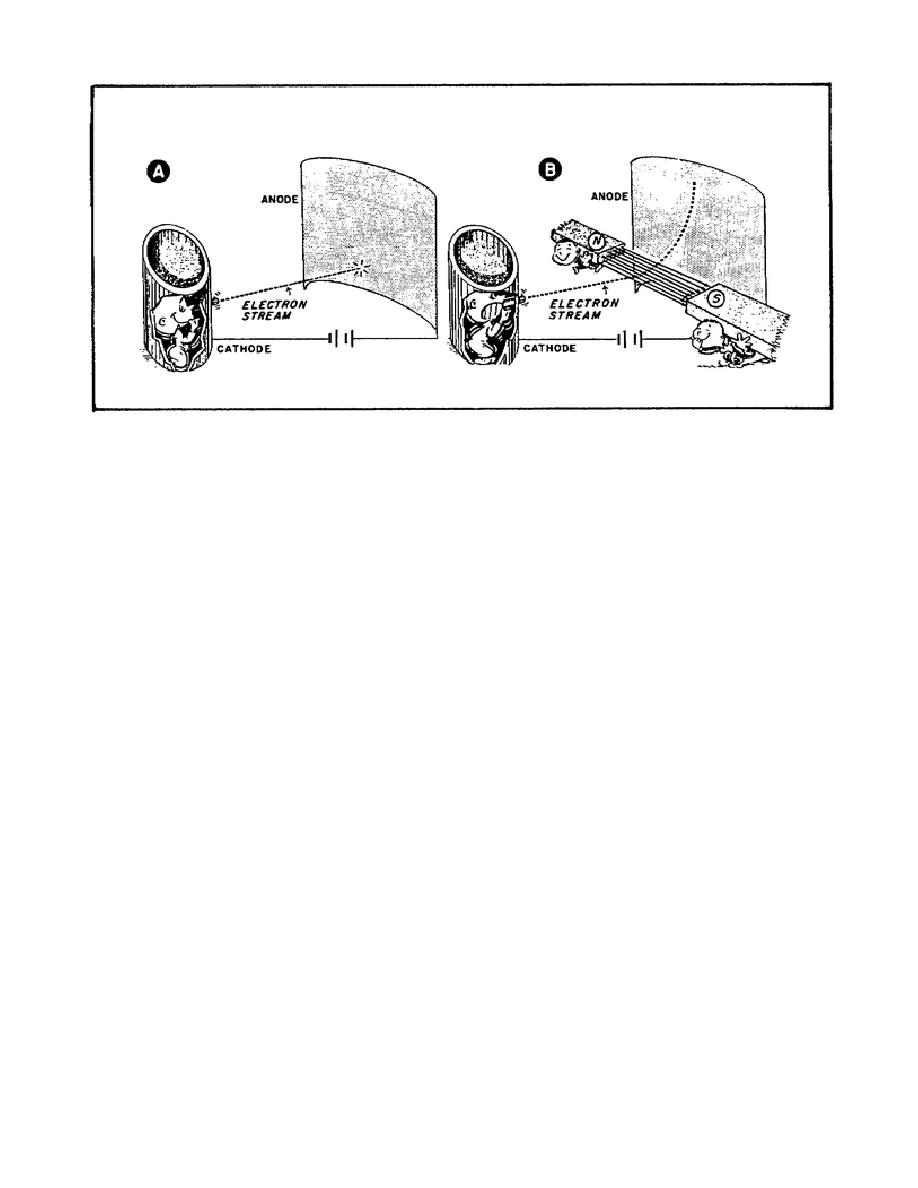
Figure 90. How a Permanent Magnet Moves
Electrons in a Diode.
b. Now notice what happens to the electron flow when we add a permanent
magnet to the diode as in Part B of Figure 90. Instead of traveling to the
plate in a straight path, the electrons take a curved path. Why does the
permanent magnet have this effect on electron flow? Well, you remember how
a permanent magnet moves a wire that has electrons flowing through it. The
wire moves because the magnetic field around the electrons inside the wire
interact with the magnetic field of the magnet. It's the same thing here,
the electrons traveling through the space between the cathode and plate have
the same kind of magnetic field around them as the electrons moving through
a wire. Therefore, the permanent magnet affects the electrons moving from
cathode to plate in the same way.
Thus, the permanent magnet makes the
electrons move in a curved path toward the plate.
14. Strength of magnet and cathode voltage determine electron path.
Now let's see what happens if we use different size magnets and
different values of cathode voltage. First we will keep the same voltage on
the cathode and vary the magnetic field strength. You can see in Part A of
Figure 91 that the greater the force of the magnet, the greater is the arc
in which electrons travel from cathode to anode. In fact, if the magnetic
field is too strong, the electrons double back to the cathode and never
reach the anode.
130



 Previous Page
Previous Page
