d. An example of resonant cavity feed is shown in Part C of Figure 139.
In this method, called cutler feed, the waveguide transmission line
terminates in a tunable resonant cavity. You tune the resonant cavity using
the adjustable screw in the rear. RF energy comes out of the cavity through
the two slots in the front and bounces off the reflector as it did with the
other feed methods.
e. Now you know how RF energy is fed to the reflector.
Next, let's
find out how the reflector forms the RF energy into a beam.
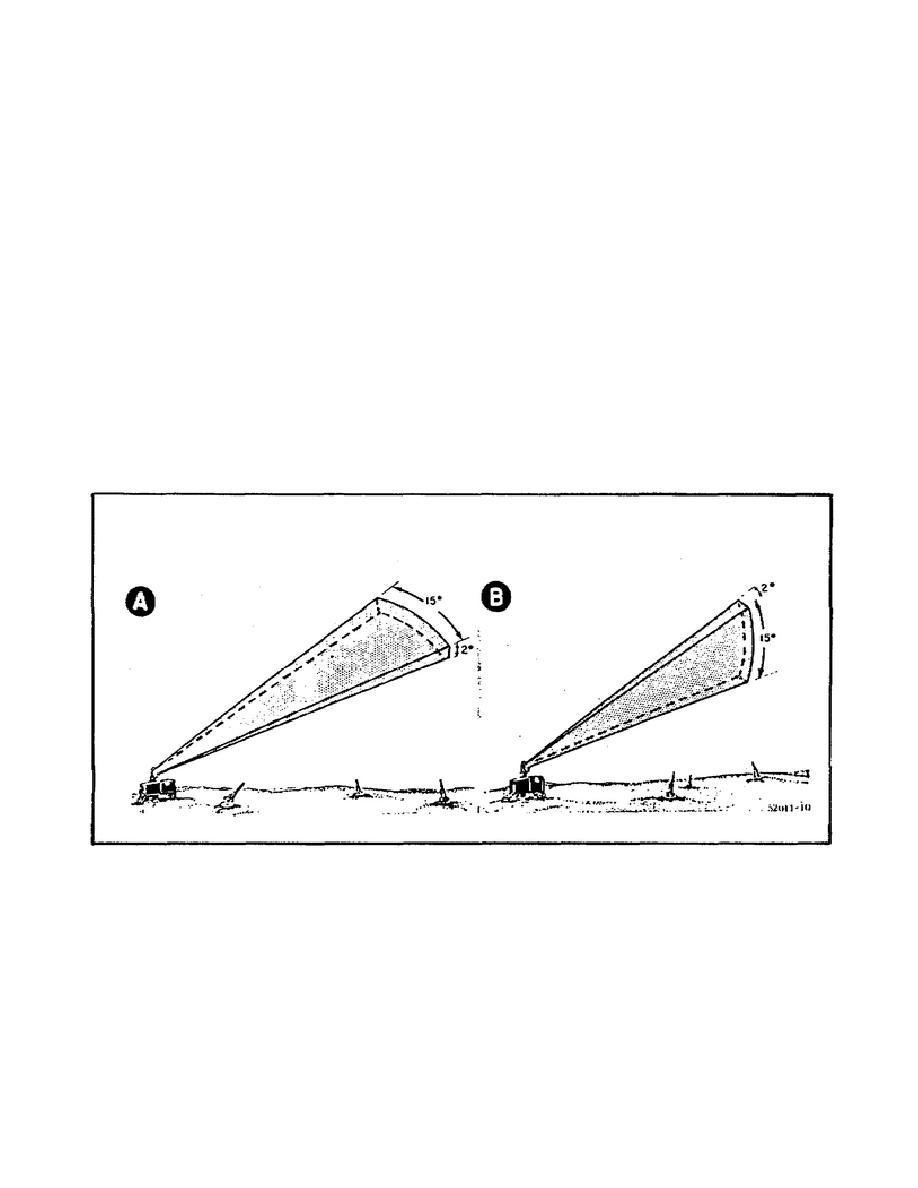
15. Antenna radiation pattern is called a beam.
a. You know that the light directed from a flashlight is called a beam;
so is the energy radiated from a radar antenna. The width of a radar beam
is measured in degrees in two directions, horizontally (parallel to the
earth), and vertically (perpendicular to the earth). Figure 140 shows you
the beamwidth of two antennas.
b. The antenna in Part A of Figure 140 has a vertical beamwidth of two
degrees and a horizontal beamwidth of fifteen degrees.
Because of these
dimensions, we say the beam is narrow vertically and broad horizontally.
Figure 140.
Broad and Narrow Radar Beams.
c. The other antenna in Part B of Figure 140 has a horizontal beamwidth
of 2 degrees and vertical beamwidth of 15 degrees. Therefore, we say this
antenna has a beam that is narrow horizontally and broad vertically.
195



 Previous Page
Previous Page
