ATTACHED MEMORANDUM
1-1.
GENERAL INFORMATION
frequencies
either
from
a
single
frequency source or from
a
minimum
a. Modern multichannel communi-
number of sources.
cation
equipment
requires
many
1-3.
BASIC
FREQUENCY
SYNTHESIS
different signal voltages to process
PRINCIPLE
the intelligence being transmitted.
For example, to transmit voice signals
over
a
multichannel
system,
each
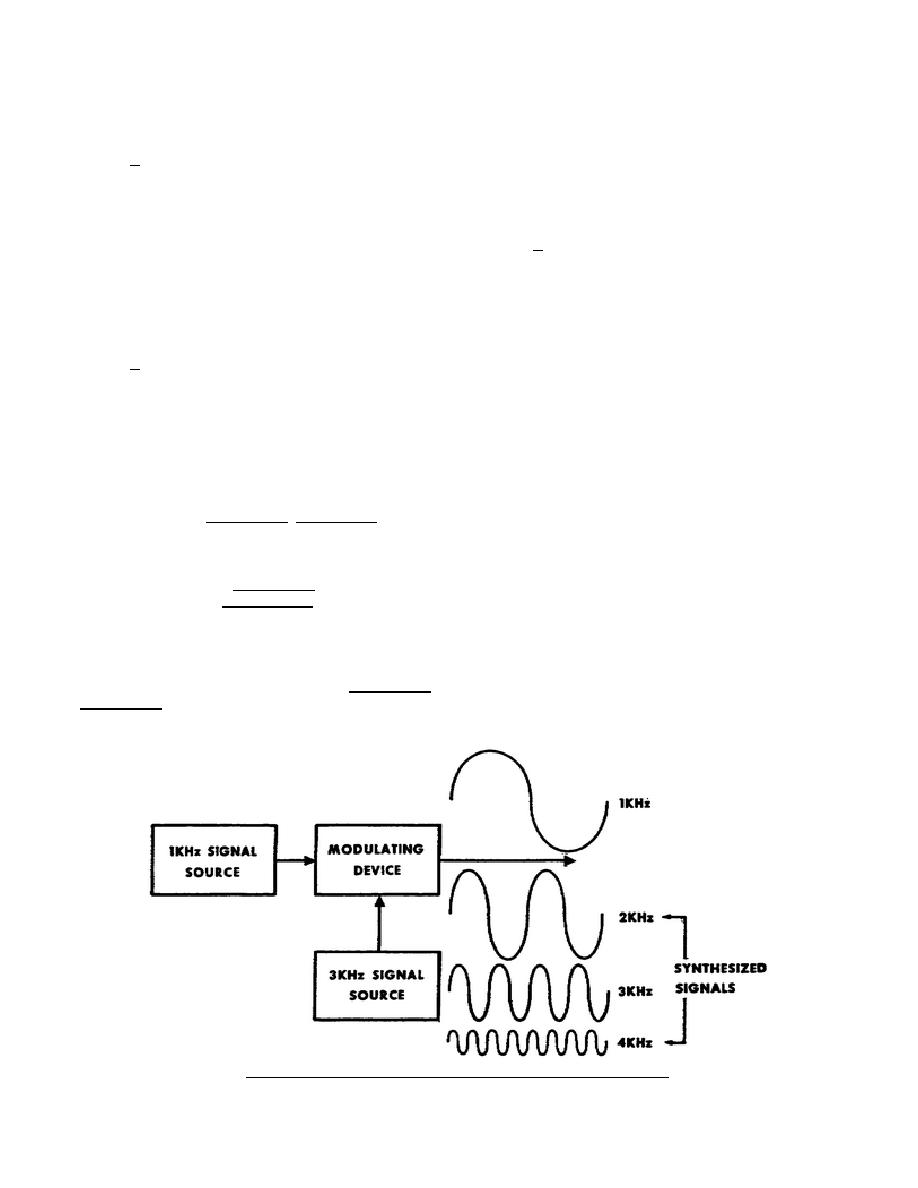
a. To
produce
a
synthesized
channel modulator must be supplied
signal, all you have to do is apply
with a carrier signal. And to prevent
two signals of different frequencies
channel interference, each of the
to a non-linear device.
For example,
carrier signals must be a different
if you apply a 1 kiloHertz (kHz)
frequency and extremely stable.
signal an a 3 kHz signal to the
modulator shown in figure 1, you get
b. In addition to the carrier
the following output signals.
signals, a system may also require
signal voltages for testing, alarms,
(1) 1 kHz.
ringing, and synchronization.
The
methods used to produce these various
(2) 2 kHz.
signals may vary--it depends on the
specific
requirements.
From
the
(3) 3 kHz.
standpoint
of
economy
and
space,
however, the most practical is a
(4) 4 kHz.
method called frequency synthesis.
b. The 2 kHz and the 4 kHz
1-2.
WHAT FREQUENCY SYNTHESIS MEANS
signals are the synthesized signals,
and the other two signals are, of
The word synthesis is derived
course, the two original signals.
b
from the word synthetic, which means
other words, a synthesized signal is
artificial,
not
original,
or
not
nothing more than the upper or lower
genuine.
Synthesis on the other hand
sideband output from a modulating
means a composition, or combination of
device.
This is the same principle
parts (elements) that form a whole.
used in communication equipment to
It
follows
then
that
frequency
develop all the various signals that
synthesis must refer to the process of
are needed to make the equipment work
obtaining several different synthetic
properly.
Figure 1.
Basic frequency synthesis principle.
327 L1
3



 Previous Page
Previous Page
