1-4.
SYNTHESIZING METHODS
the harmonic generation is used to
great advantage.
Other applications
a. There
are
several
different
require variable output signals, as in
methods, or combinations of methods
radio transmitters and receivers.
In
that
produce
synthesized
signals.
these cases any or all three methods
But, all of these methods are divided
may be used, but one or both original
into three general classes as follows:
signal sources must be adjustable.
1-5.
HOW THE BASIC MODULATION METHOD
(1) Basic
Modulation
Method.
WORKS
This method is the same method shown
in figure 1.
It uses conventional
modulating devices, such as electron
The basic modulation method is
tubes, transistors, or varistors.
exactly the same process that uses
voice to modulate a carrier signal as
(2) Harmonic Generation Method.
shown by the block diagram in figure
Produces two or more signals from the
2.
The output signals, as you know,
same source, then modulates these
depend
on
the
input
signals
and
signals to produce a large number of
whether the modulator is balanced or
noise free synthesized signals.
The
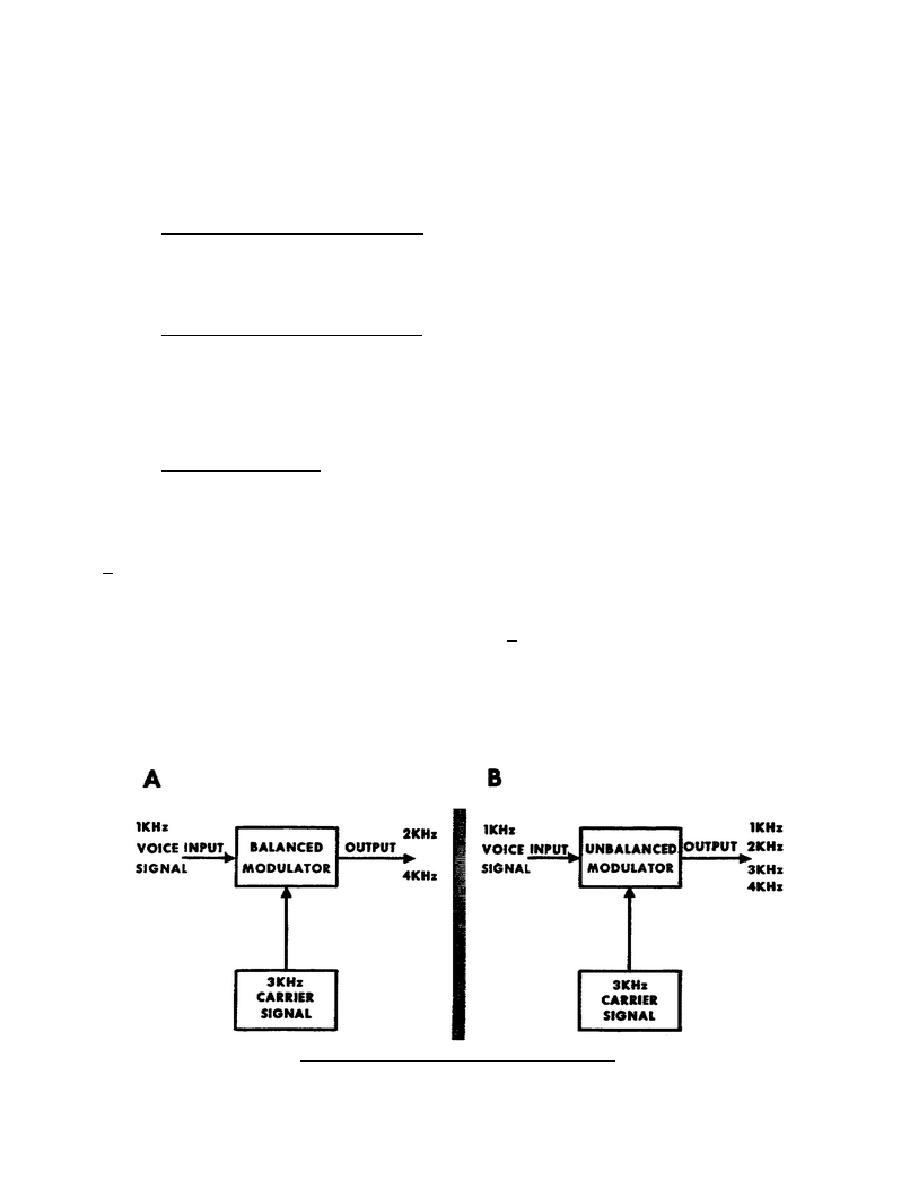
unbalanced.
For example, if the
modulator in this case is identical to
signals into a balanced modulator are
the one described above.
1 kHz and 3 kHz, then there are only
two output signals--2 kHz and 4 kHz
(3) Heterodyne Method.
Produces
(A, fig 2).
However, if the original
a single synthesized signal.
All
signals are applied to an unbalanced
spurious and unwanted frequencies are
modulator, you get four signals at the
suppressed by using the heterodyning
output.
In this case these signals
principle as a filtering process.
are 1 kHz, 2 kHz, 3 kHz, and 4 kHz (B,
fig 2).
b. The method, or combination of
1-6.
HOW
THE
HARMONIC
GENERATION
methods used in a specific application
METHOD WORKS
depends on the requirement.
For
example, if a large number of signals
are required, chances are the harmonic
a. To generate harmonics, you must
generation method is used.
If a
apply the fundamental frequency to a
harmonic and noise free signal is
nonlinear device.
A common method is
required then the heterodyne method is
to apply the signal to an electron
used.
Some applications require many
tube biased to operate as a class b or
fixed
signals,
such
as
telephone
multiplex equipment. In these cases
Figure 2.
Basis modulation method.
327 L1
4



 Previous Page
Previous Page
