c. In this lesson, you will study the properties and characteristics of
transmission lines used to guide RF energy from source to load. Also, you
will learn how transmission lines are used as circuit components.
For
example, you will learn how a section of transmission line is used as an
impedance-matching transformer and how a small length of line is used as the
tank circuit in an UHF oscillator.
These applications are especially
important in the fields of radar and microwave.
2.
First, a few terms.
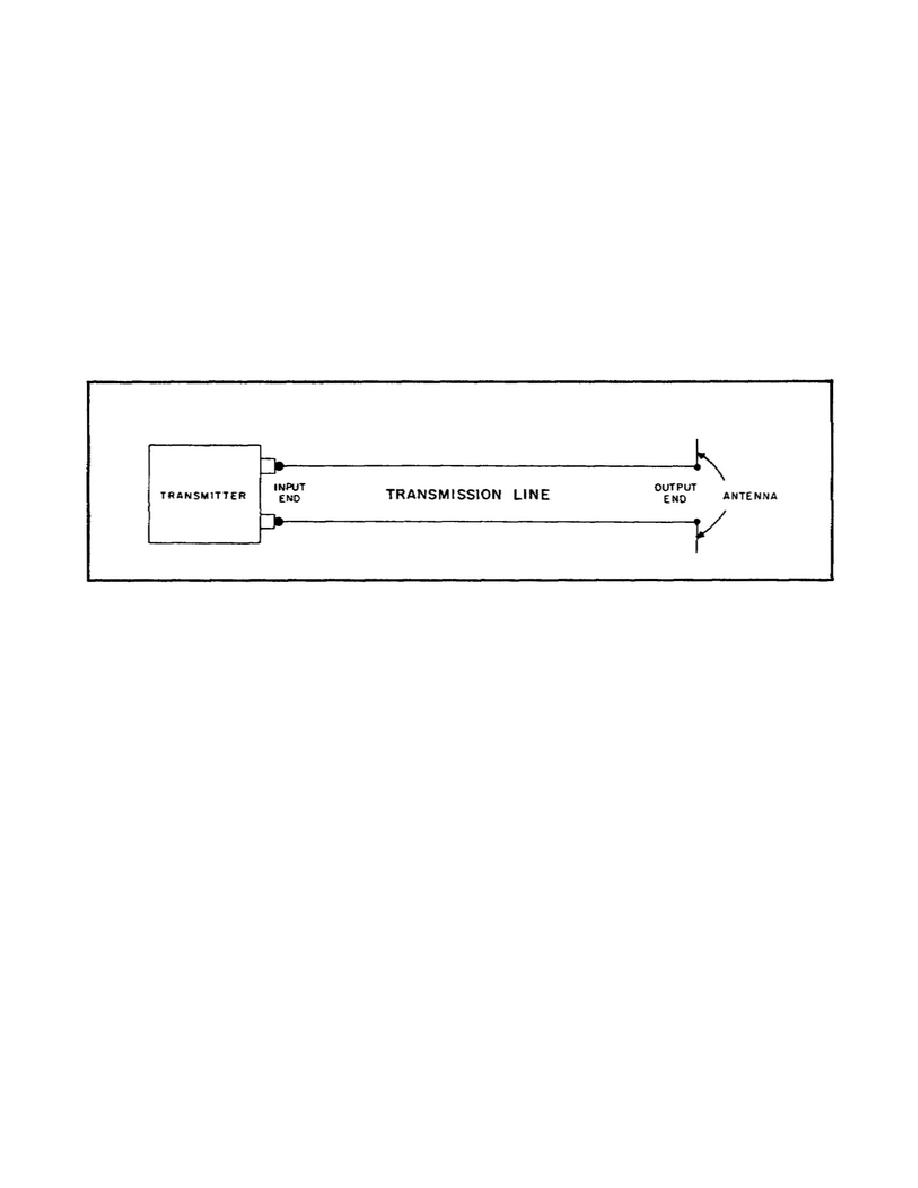
a. Figure 1 shows a transmission line used to couple RF energy from a
transmitter to the antenna of a communications system.
The transmission
line has an INPUT END and an OUTPUT END. The transmitter is coupled to the
input end, also called the generator end or source. The antenna is coupled
to the output end, also called the load end or sink.
Figure 1.
Basic Transmission System.
b. A transmission line can be called long or short.
A transmission
line is long when its length is long compared to the wavelength of the RF
signal place on it by the source.
It is short when its length is short
compared to the wavelength. The long-short concept is an important one for
you to understand, for it explains why a piece of wire can act as a tank
circuit at ultra-high frequencies.
3.
When is a transmission line long?
A transmission line is long when its length is long compared to the
wavelength of the frequency used. It is not just the physical length alone,
but rather the ratio of physical length to the wavelength.
For example,
look at Part A of Figure 2 which shows a generator coupled to a transmission
line. The length of the transmission line is 12 inches. Now, 12 inches of
transmission line doesn't seem long when you compare its length to that of
the room you're in. But when you compare this 1 foot of transmission line
to the wavelength of 3000 megahertz, you find that the line isn't so
2



 Previous Page
Previous Page
