b. One means by which we can study transmission lines is to use an
equivalent circuit.
This is easy to do because RF transmission lines are
similar to ordinary circuits in all respects except for their length.
Ordinary circuits contain "lumped properties;" that is, actual physical
components.
RF transmission lines also have resistance, capacitance, and
But these components appear in the form of "distributed
properties." When you understand the equivalent circuit of a simple type of
transmission line, such as a parallel pair, then you will have a clearer
understanding of other types of lines.
c. First, consider what a parallel pair transmission line is.
It
consists of two wires of constant diameter, evenly spaced, and running
parallel. By representing this line as a simple equivalent circuits, we can
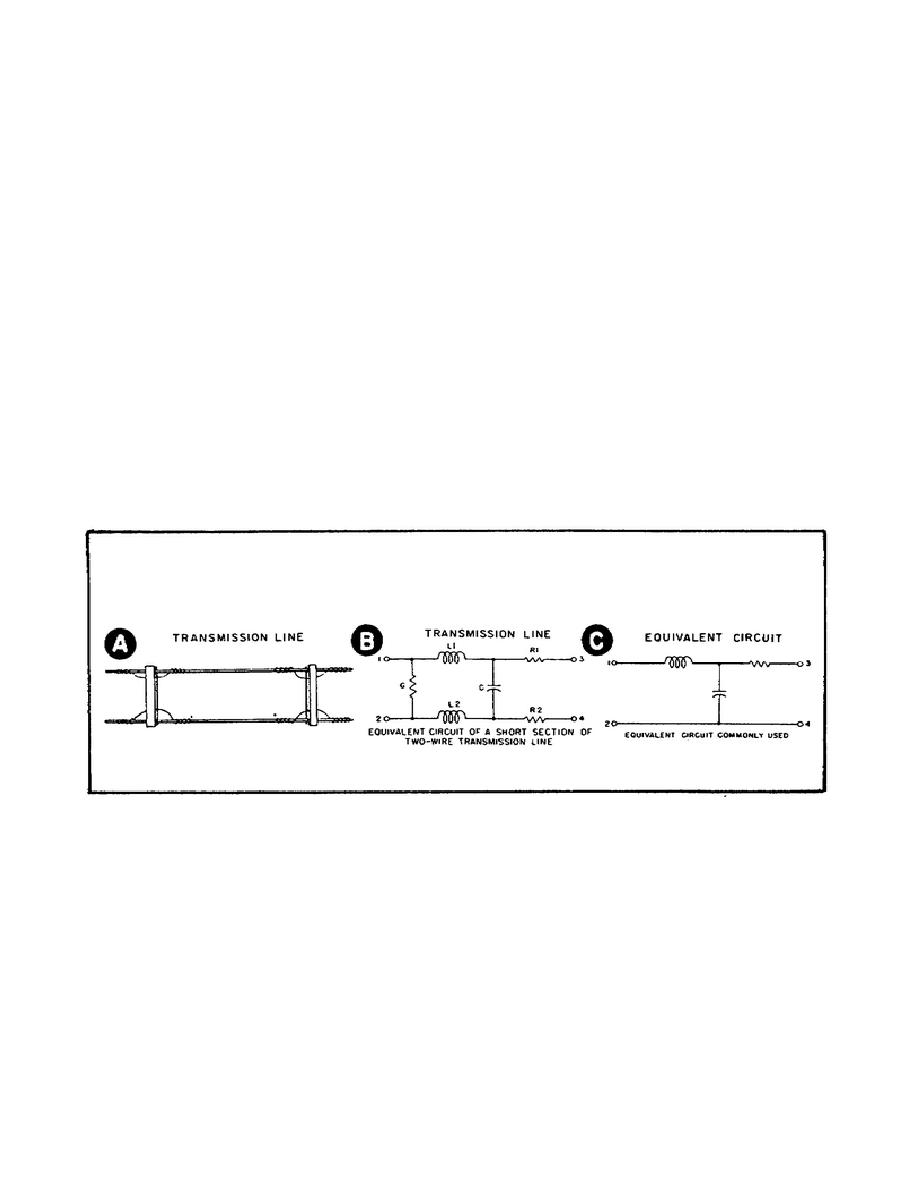
analyze it more easily. Figure 7 shows a parallel pair transmission line
and its equivalent circuit.
Notice in Part B of Figure 7 that the
transmission line has resistance and inductance in series with the line.
There is capacitance between the conductors regardless of the spacing
between the wires.
Also, there is a high-resistance (G), low-conductance
leakage path between the two conductors because no material is a perfect
insulator.
Keep in mind that the line does not contain actual physical
resistors, capacitors, and inductors.
Instead, the properties are
distributed throughout the line.
Part C of Figure 7 shows the equivalent
circuit commonly used.
Figure 7.
The Electrical Equivalent of a Transmission Line.
d. As you know, all AC circuits have an opposition to the flow of
alternating current. This opposition is called impedance. A transmission
line also has impedance.
13. A transmission line has a characteristic impedance.
8



 Previous Page
Previous Page
