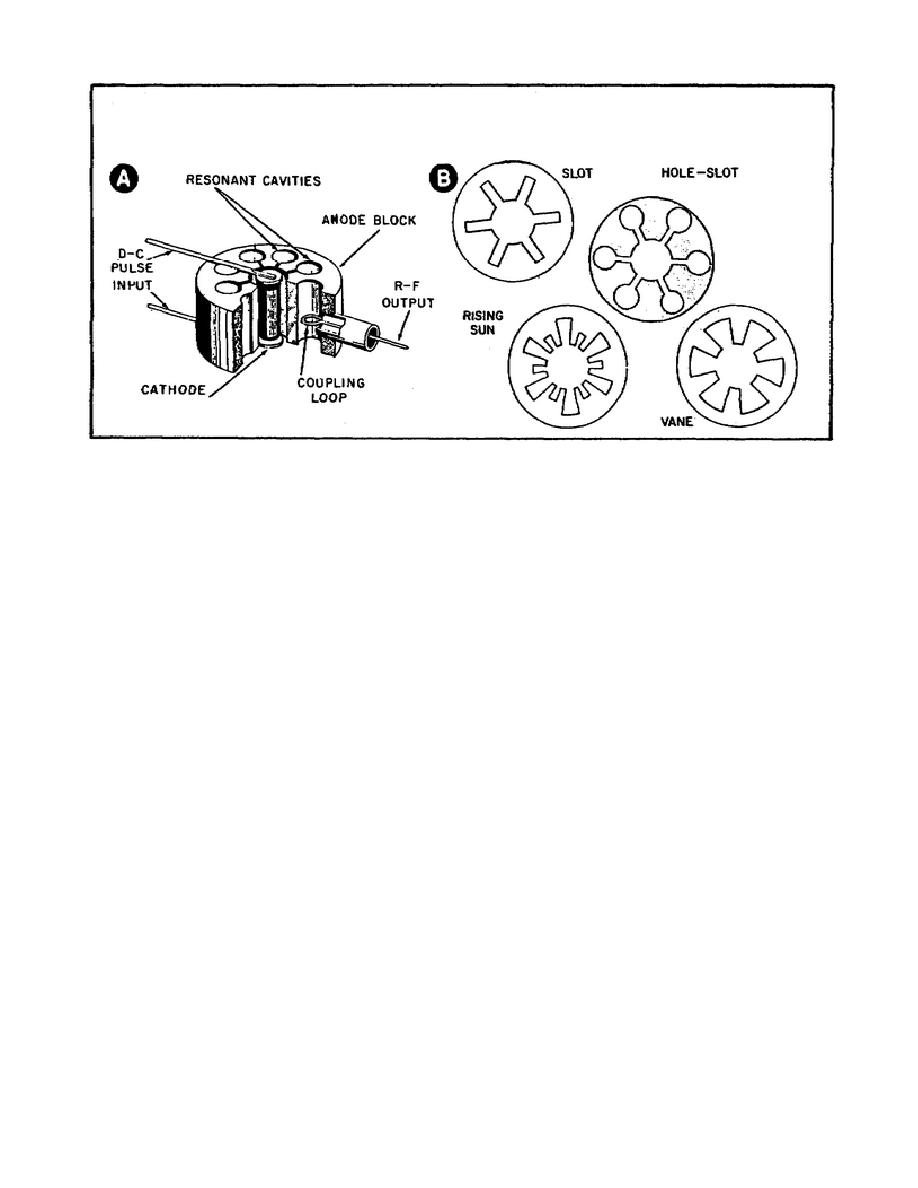
Figure 85.
Internal View of the Resonant
Cavity Magnetron.
f. The sections of the anode block that are between the cavities are
called segments, and the space between the cathode and anode block is called
the interaction space. It is in this space that the high-voltage, DC pulse
from the modulator is converted into the RF carrier.
3.
How energy is coupled out of a magnetron.
Notice the coupling loop in Part A of Figure 85.
It is used to
couple energy out of the magnetron.
You might think at first that there
should be a loop in each cavity. But, remember that the cavities are all in
parallel, and when we couple energy from one cavity, we are actually
coupling energy from all the cavities. Sometimes, instead of coupling the
RF energy out of the magnetron with a loop, we just couple it out through a
Slot.
As with loop coupling, it is necessary to have a slot in only one
cavity.
4.
The outside construction of a magnetron.
a. Part A of Figure 86 shows the outside of the 5J26 magnetron and its
magnet.
The 5J26 is used in radar set AN/TPS-1D.
You can see that the
magnet is a permanent horseshoe type and is separate from the tube. Most
magnetron magnets are made of ALNICO, which is a combination of aluminum,
nickel, and iron. ALNICO is used for permanent magnets because it holds its
magnetism indefinitely.
123



 Previous Page
Previous Page
