SM0486
(2) You can make conversions to the Kelvin and Rankin scales using the
relations:
K = 273.16 + C.
R = 459.69 + F.
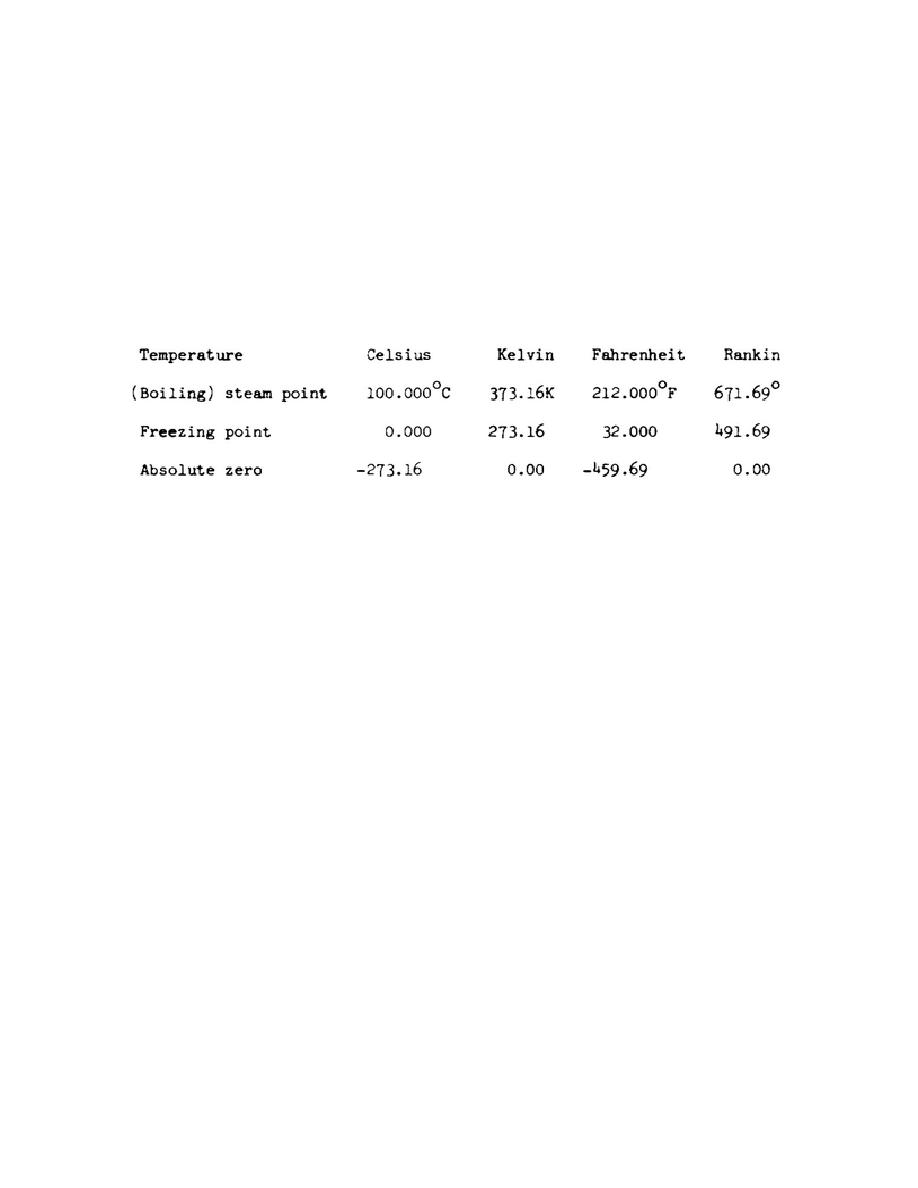
(3) Table 3 shows the differences in steam point, freezing point, and
absolute zero for the four scales shown in figure 3.
TABLE 3
Common Thermometer Scales
Mercury-in-Glass Thermometer
(4) You have been told that temperature is a measure of the intensity of
heat and that one of several scales used to indicate the intensity of heat is
usually a part of a temperature measuring instrument.
Some of the more common
practical measuring instruments are listed in table 4, with their usable ranges.
c. Mercury-in-Glass Thermometer.
(1) Table 4 includes the mercury-in-glass thermometer in the list of common
temperature measuring instruments.
In its simplest form, the mercury-in-glass
thermometer is a hollow glass tube, hermetically scaled at both ends, and expanded
into a bulb at its lower end. The bulb is filled with mercury, and most of the air
is evacuated from the tube before it is sealed.
This partial vacuum permits the
free expansion of the mercury to the top of the tube. When the mercury is heated,
it expands and rises in the tube. When the mercury is cooled, it contracts and its
level in the tube is lowered. A typical mercury-in-glass thermometer is shown in
figure 4.
9



 Previous Page
Previous Page
