SM0486
energy is the energy of molecules in motion, heat considerations must also include
the vibratory motion of molecules.
Our primary point of concern is that heat
measurements are affected by the vibratory motion of molecules and the relative
changes in their motion. An increase in the heat that a body possesses is due to
an increase in its kinetic energy.
In order to increase the molecular kinetic
energy in a body, you must increase the energy which produces the vibratory motion.
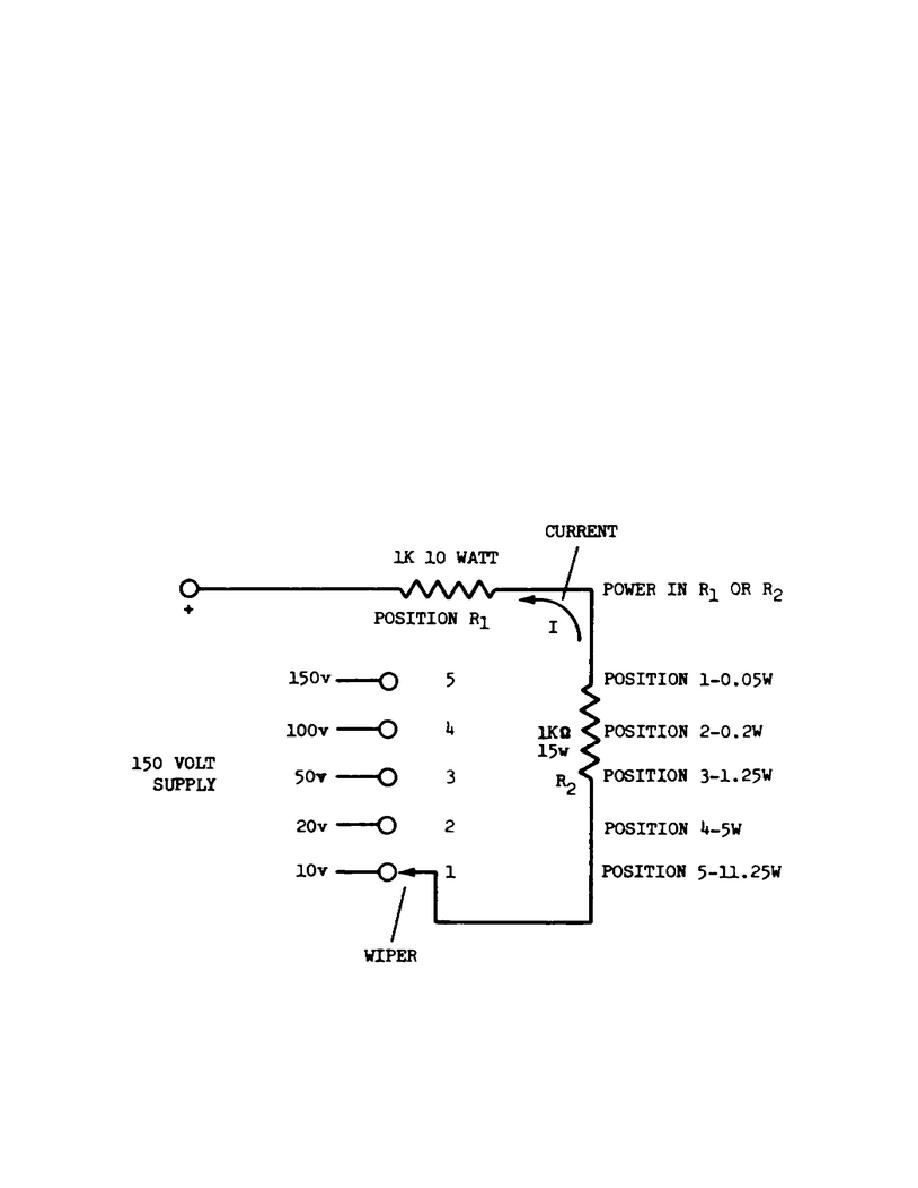
(1) The circuit in Figure 2 is an example of changing the kinetic energy
(molecular vibratory motion) level of components (resistors) in an electrical
circuit.
(2) From the circuit in Figure 2, you can see that the only factor,
affecting the power (kinetic energy) dissipated by the resistors are the voltage
(E) and the current (I). It is a simple series circuit in which the total current
flows through each resistor.
Since the resistances are equal, the voltage drops
across the resistors are equal, and each resistor dissipates the same amount of
power.
This means that the power values listed in figure 2 apply to R1 and R2.
The differences in power values listed in figure 2 represent the changes in applied
power (voltage and current) caused by changes in the power switch position.
The
resulting changes in power values (kinetic energy) also represent changes in the
energy losses in the form of heat. Table 2 is included to help you understand how
changes in the values of power applied to a circuit (or body) produce changes in
the kinetic energy of that body.
Figure 2.
Energy, heat, and power in an electrical circuit.
5



 Previous Page
Previous Page
