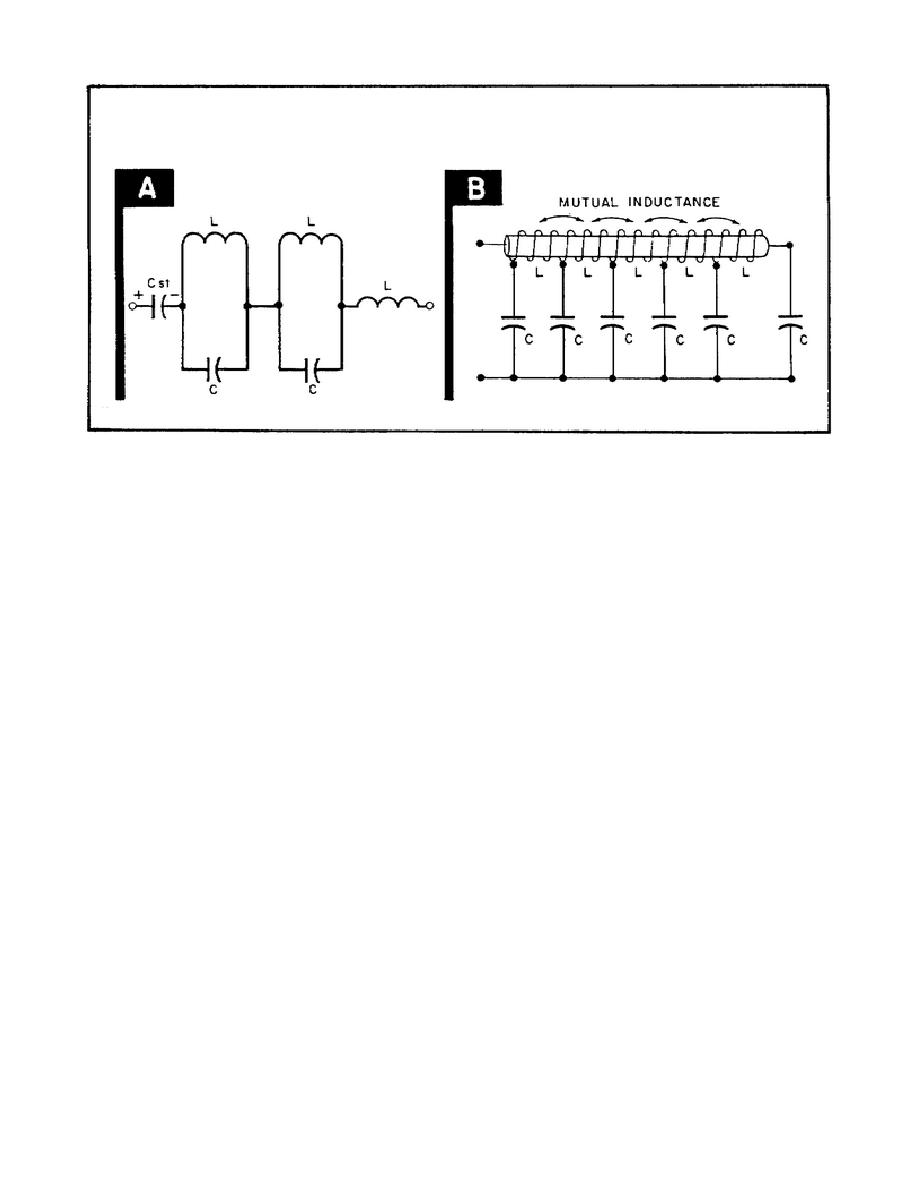
Figure 55. Two Types of Guillemin Lines
Used as Pulse-Forming Networks.
6. Part B of Figure 55 shows an open-end artificial transmission line with
magnetic coupling between the coils.
Mutual inductance is used to remove
undesirable oscillations on the top of the pulse. Notice that the line is
actually a long solenoid with tap points for equal-value capacitors.
The
combination of all capacitors in parallel makes up the storage capacitor.
This type of PFN is the one used most frequently in modern radar systems.
7. Pulse-forming networks are usually "potted," sealed in an oil-filled
metal container. The oil is used for compact high voltage insulation. You
can see, then, that there is no maintenance to be done on the PFN. If one
of the elements of the line fails, you must replace the entire line.
8.
Brief review.
a. Most modern radar sets use the high-level modulation system in which
the pulse is formed at a high power level.
b. In high-level modulation, the pulse is formed by discharging a
pulse-forming line through a load resistance equal to the characteristic
resistance of the line.
c. The PFN determines the shape and width of the pulse.
d. The amplitude of the pulse is equal to one-half the voltage to which
the line is charged.
e. The pulse width is equal to two TDs.
f. The PFN is discharged at the pulse repetition frequency of the
radar.
68



 Previous Page
Previous Page
