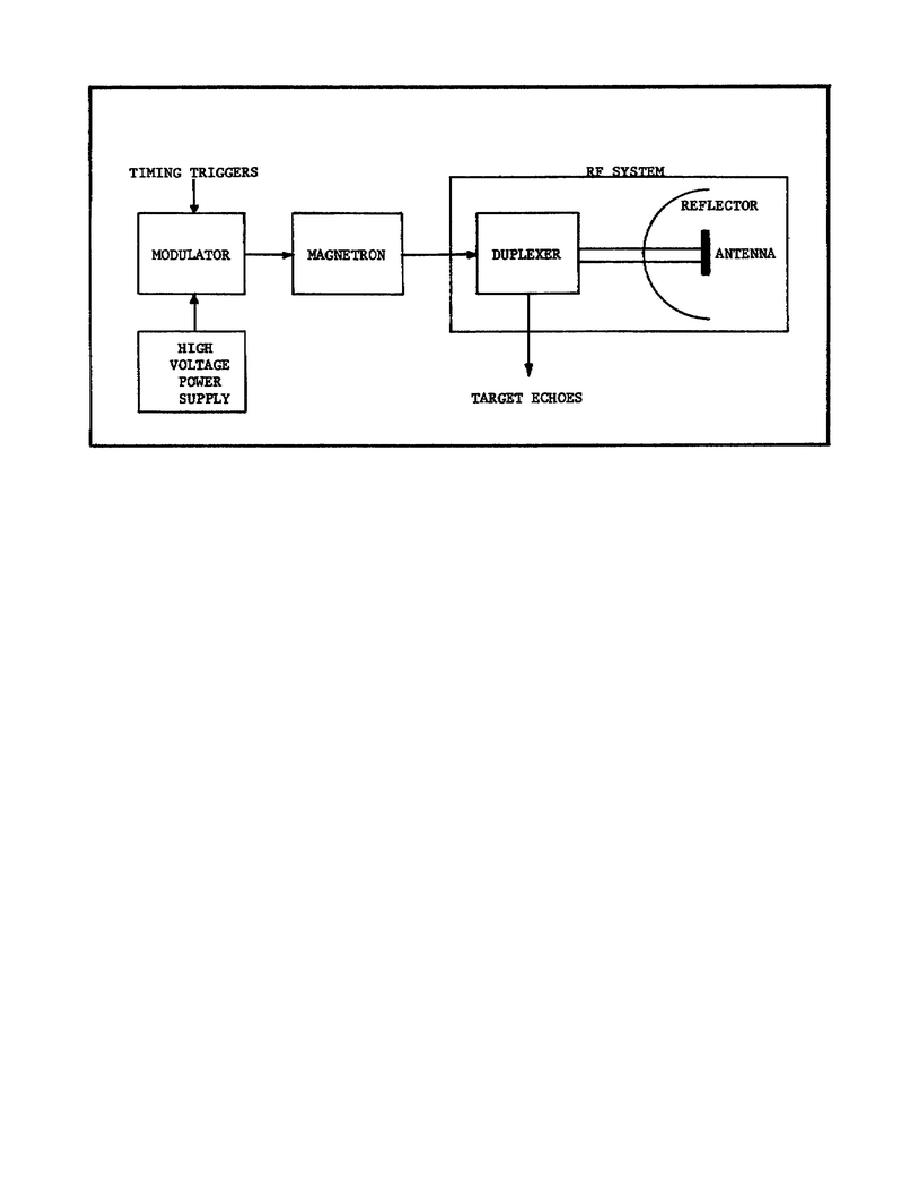
Figure 52. Basic Radar Transmitter.
(1) High-voltage power supply. The high-voltage power supply is used
to charge the pulse-forming line in the modulator.
Switches, relays, and
interlocks are used in conjunction with the power supply to control the
application of voltages, prevent overloads from damaging components, and to
protect personnel from the high voltages.
(2) Modulator. The modulator controls the operation of the magnetron
by supplying it with the high-voltage rectangular pulses of DC. In effect,
the modulator acts as the power supply for the magnetron.
When the
modulator output is applied to the magnetron, the magnetron oscillates.
When the pulse is removed, the magnetron stops oscillating. The modulator
acts like a switch that turns the magnetron on and off.
(3) Magnetron. The magnetron is really the heart of the transmitter
because it is a high-power, high-frequency oscillator that produces bursts
of RF energy for short periods of time. The time that the magnetron is on
is very short as compared to the time that it is not oscillating. When the
magnetron is pulsed, it generates short bursts of RF energy. The frequency
at which the magnetron is pulsed, that is, turned on and off, is known as
the pulse repetition frequency (PRF) and the frequency at which the
magnetron oscillates is known as the carrier frequency.
63



 Previous Page
Previous Page
