degree turn. The mitered bend must be at least one-quarter wavelength long
between the two points indicated. Both bends result in a 90 degree turn,
but they are gradual (not sharp) turns.
We make the bends gradual to
prevent reflections that cause power loss. Bends in rectangular waveguide
are further classified as E or H bends.
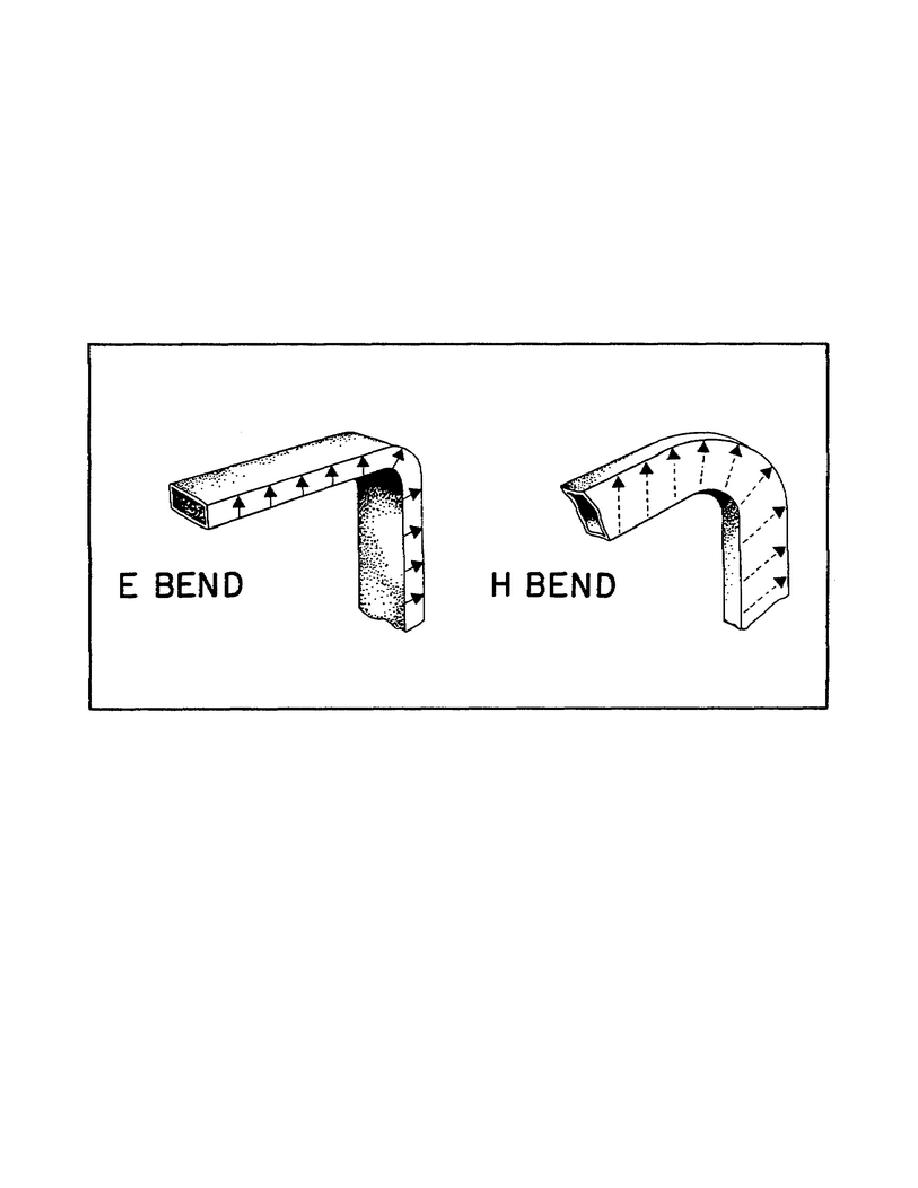
24. What are E and H bends?
Figure 122 shows both E and H waveguide bends. An E bend is one in
which the waveguide is bent in the plane of the electric field. An H bend
is one in which the waveguide is bent in the plane of the magnetic field.
Figure 122 shows how the E and H fields change from a horizontal to a
vertical plane in their respective bends.
Figure 122.
E and H Bends.
25. Twisted waveguide is used to change the plane of polarization.
a. We describe the position of an electromagnetic field with respect to
the earth, using the term polarization.
If the E field is vertical with
respect to the earth, we say the electromagnetic field is polarized
horizontally.
b. Sometimes, to simplify mechanical layout, the field in a waveguide
is polarized in a different plane than the one desired at the output. To
get the proper polarization at the output of the waveguide, a twisted
section is used.
A twisted section of waveguide must be at least two
wavelengths long to prevent reflections and loss of power. Figure 123 shows
how a vertically polarized wave is changed to a horizontally polarized wave
by a twisted section of waveguide.
176



 Previous Page
Previous Page
