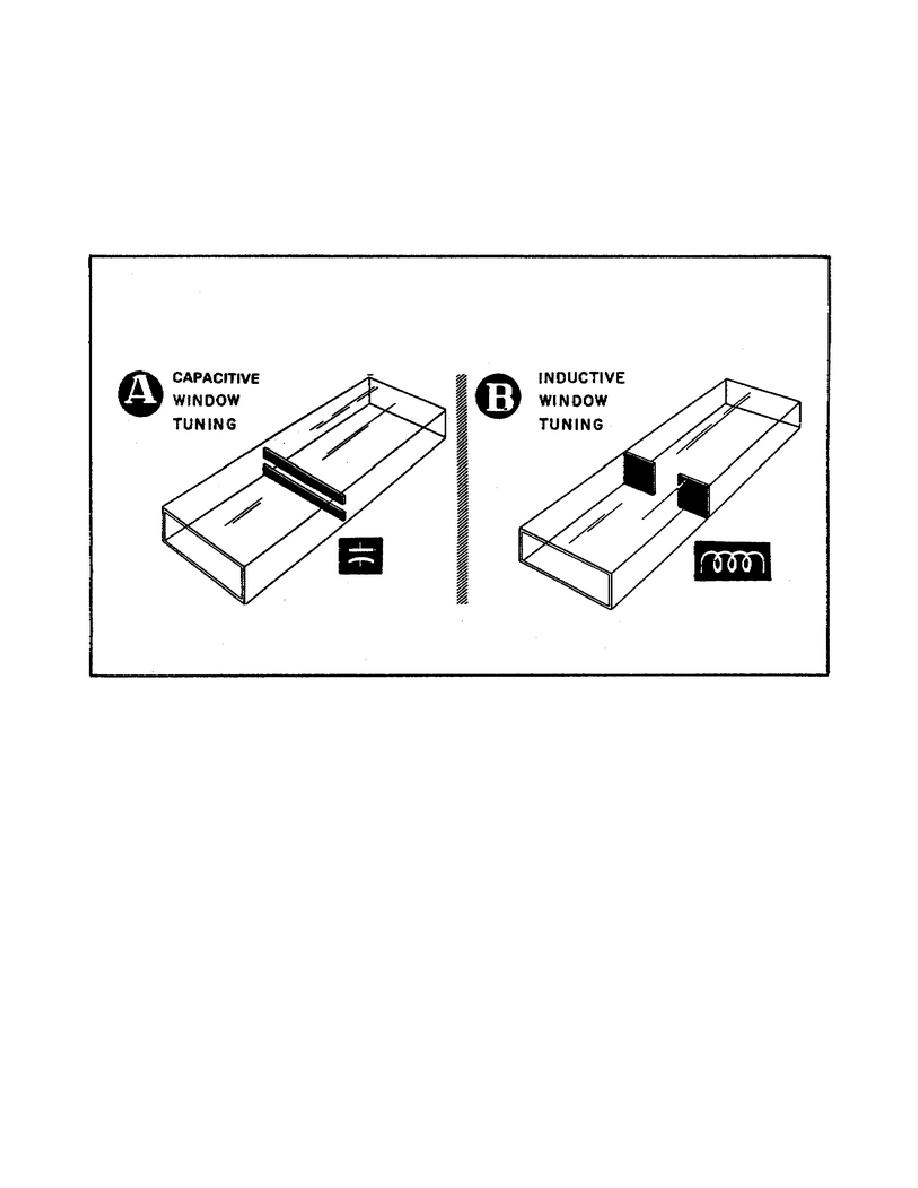
28. Fixed window tuner.
a. Figure 126 shows two metallic fins or plates placed in a waveguide
in such a way that they reduce the cross-section of the guide. The metal
partitions are reactive elements called irises. The space between the metal
plates is called a window; that's why we call it window tuning. The irises
change the impedance characteristics of the waveguide by obstructing the
electric and magnetic fields in the guide.
Figure 126.
Capacitive and Inductive
Window Tuning.
b. Part A of Figure 126 shows two metal partitions placed in a section
of waveguide so they obstruct the electric field. This type of tuning is
called capacitive window tuning.
Here is how capacitive window tuning
works. Suppose there is an undesirable inductive reactance at a particular
point in a section of waveguide.
You know that inductive and capacitive
reactances are 180 degrees out of phase with each other. So, to get rid of
the inductive reactance, all you have to do is add an equal capacitive
reactance that cancels the inductive reactance. That is what happens when
we place metal partitions across the width of the waveguide.
The irises
obstruct the passage of the electric field and act as a capacitive
reactance.
The further we extend the irises into the waveguide, the more
capacitive reactance we add at that point.
179



 Previous Page
Previous Page
