types because of their lower internal capacitance and their excellent gain at
frequencies up to several megahertz. Low-power transistors can be either the PNP
or NPN variety, and are usually found in RF and IF amplifiers, oscillators, mixers,
detectors, and preamplifiers.
High-power transistors are usually of the PNP
variety, and are used as either single-ended class A, or as push-pull class AB or
class B audio output amplifiers.
2-2.
RF AMPLIFIER
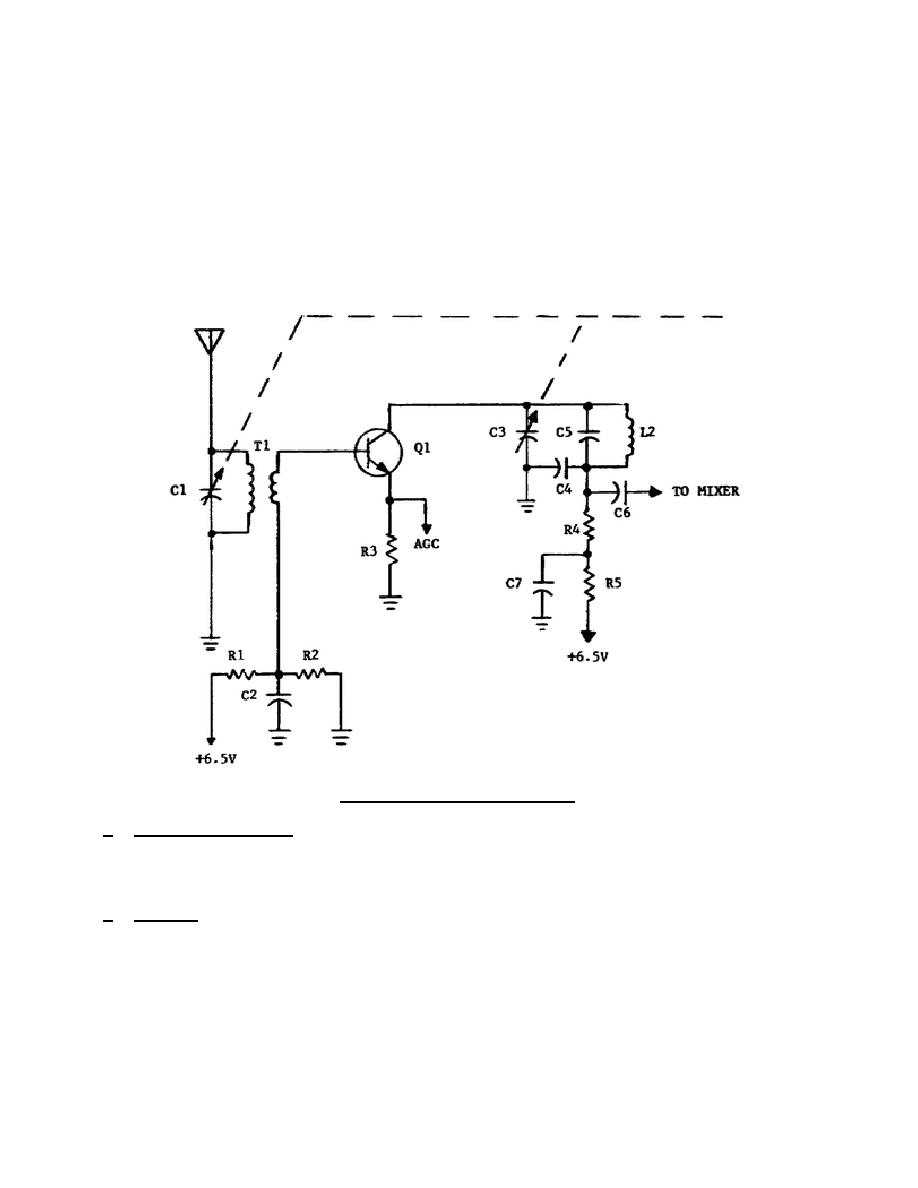
A transistorized RF amplifier is shown in figure 2-1.
This amplifier uses an
NPN transistor in a grounded-emitter circuit in which the emitter is common to both
the input and output circuits.
Figure 2-1.
a. Input Signal Path.
The antenna input signal is coupled through transformer
T1 to the base of the transistor. The T1 is a voltage stepdown transformer that is
used at this point to match the low-impedance emitter-base junction to the high
b. Biasing. A forward bias voltage of +2.5 volts is developed by the voltage-
divider network, consisting of resistors R1 and R2, which is connected in series
with the +6.5-volt supply.
This positive bias voltage causes electrons to flow
from emitter to collector, resulting in collector current through L2, R4, and R5.
The collector current and a very small base current return
322 L2
7



 Previous Page
Previous Page
