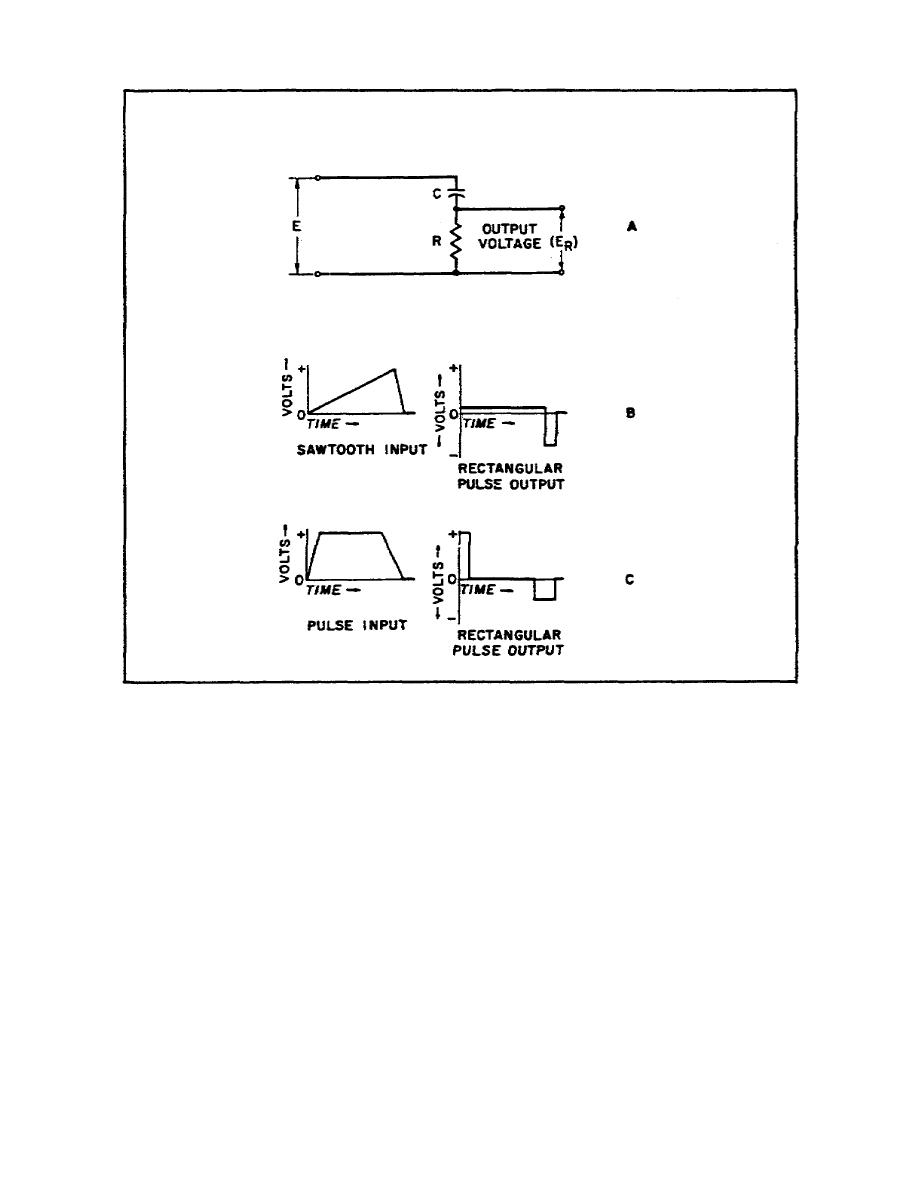
Figure 42. Differentiator circuit output for
common waveforms
e. In Figure 42C, the input to the differentiator circuit is a
rectangular pulse with finite rise and decay times. Since the
voltage rises at a constant rate to some maximum value, the input
voltage rate of change is constant. After the differentiated output
voltage reaches a steady state, it becomes a positive DC voltage
whose amplitude is proportional to the voltage rate of change and the
time constant. When the maximum value of the input voltage is
reached, the differentiated output voltage drops instantaneously to
zero since the input voltage rate of change is zero. The output
voltage remains at zero during the input voltage duration period.
During the input voltage decay period, the rate of input voltage
decrease is constant and the differentiated output voltage during
this time is a negative DC voltage. Since the input voltage rate of
change is greater during the rise time than it is during the decay
time, the amplitude of the positive DC differentiated output voltage
is greater than the negative pulse.
83



 Previous Page
Previous Page
